top of page
These images are a collection of my work throughout the years. All of the images in this gallery were acquired with various modalities. The images displayed here are a mix of my experimental design and implementation as well as work that I have acquired consulting for various clients. All of the images in this gallery were personally acquired and prepared for publication.
Images
 FFT Bandpass filter - top hat filterHeLa Cells acquired with confocal and compressed into maximum projection. Red signal is mCherry-tubulin. | 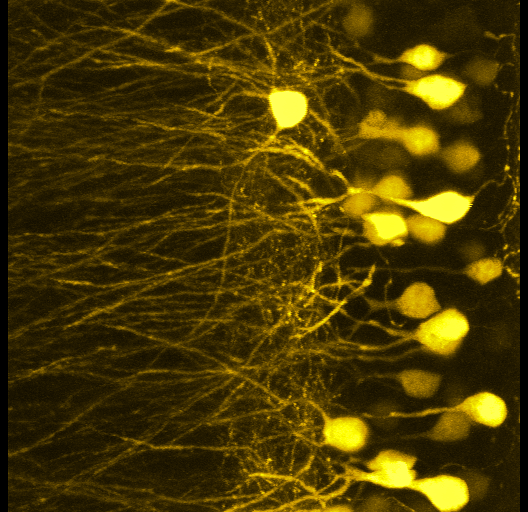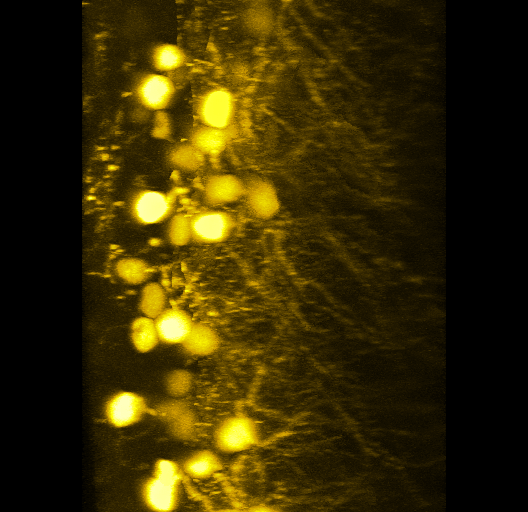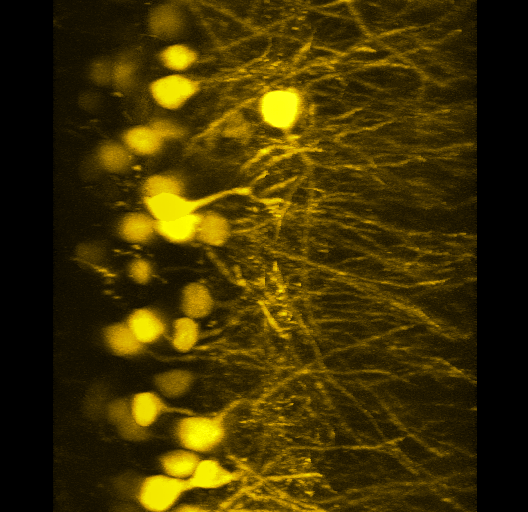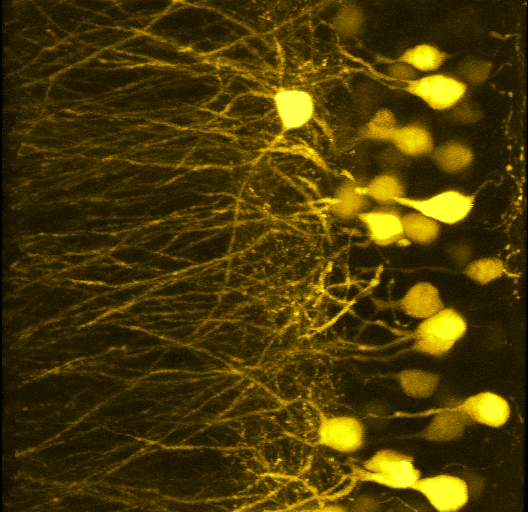 3D Neural ImagingIn complex model systems, such as the brain, it can be imperative to acquire images with high spatial resolution in X, Y and Z. Instruments such as confocal microscopes allow researchers to gain such access. |  Developing Mouse EmbryoImaged with a stereomicroscope and a color camera. The samples were obliquely lit to provide strong contrast between image and background. |
|---|---|---|
 PSF - Point Spread FunctionsPSFs are used to define the performance of an optical system. It is common for microscopists to image sub-resolution beads of known size to determine what types of distortions are occurring in the light path. The distortions measured from the PSF can be used: pre-acquisition by correcting the light path; or post-acquisition for corrections such as pixel shifts. |  Vesicle Recycling - DrosophilaThis montage of images was taken from time-lapse microscopy vesicle recycling captured in-vivo. These images were captured from fly larvae using a confocal laser scanning microscope. |  DIC - Contrast AdjustmentsThe top image is linearly sampled across the full dynamic of the detector. The bottom two images represent the data-points with the brightness and contrast adjusted. The full dynamic range of the data cannot be fully presented within the physical limitations of the display. This is important to remember post-acquisition if your data looks different than through the oculars. |
 Drosophila - X,Y, Z Confocal 2 of 2Z slices from image 1 of 2 in grid to examine optical sectioning as a composite of all three fluorescent channels. |  Brainbow - Mouse - Confocal | 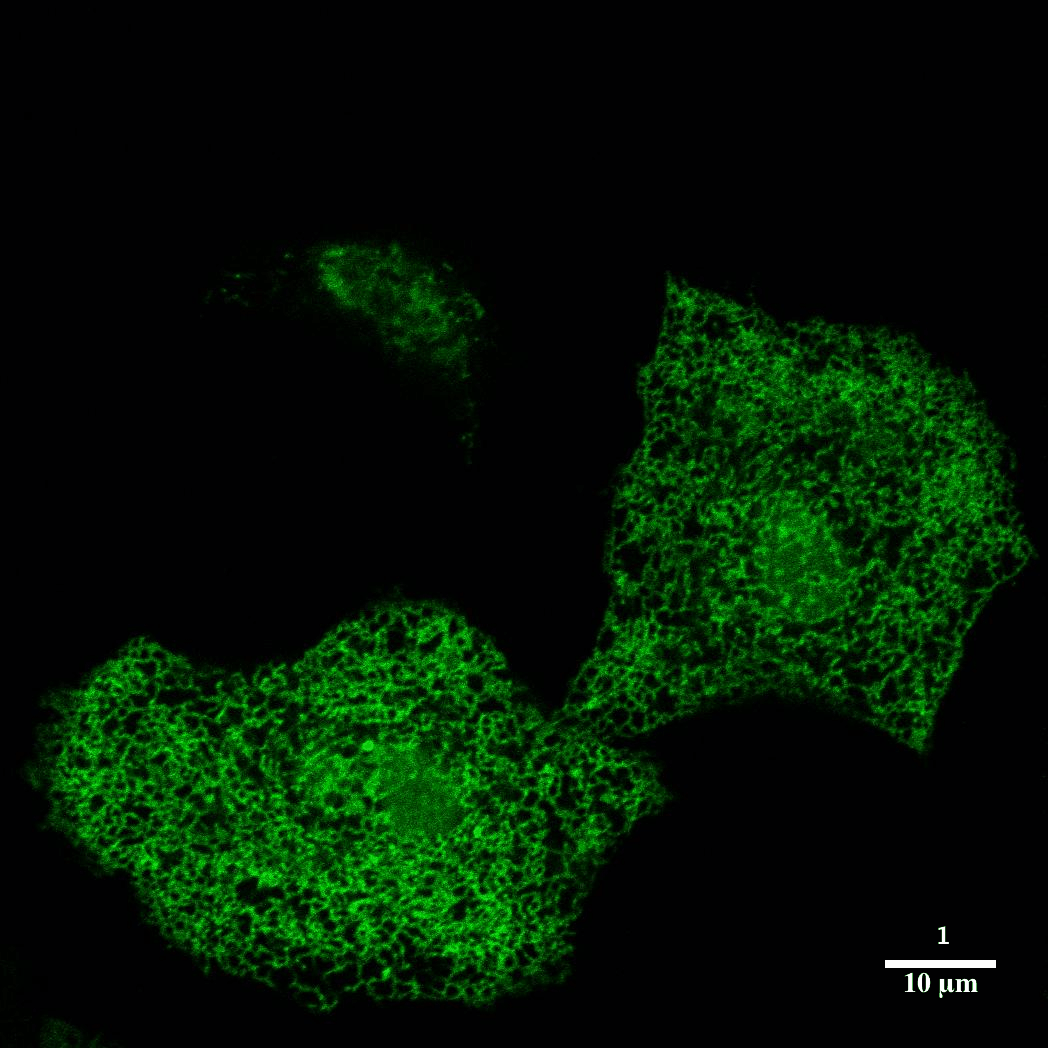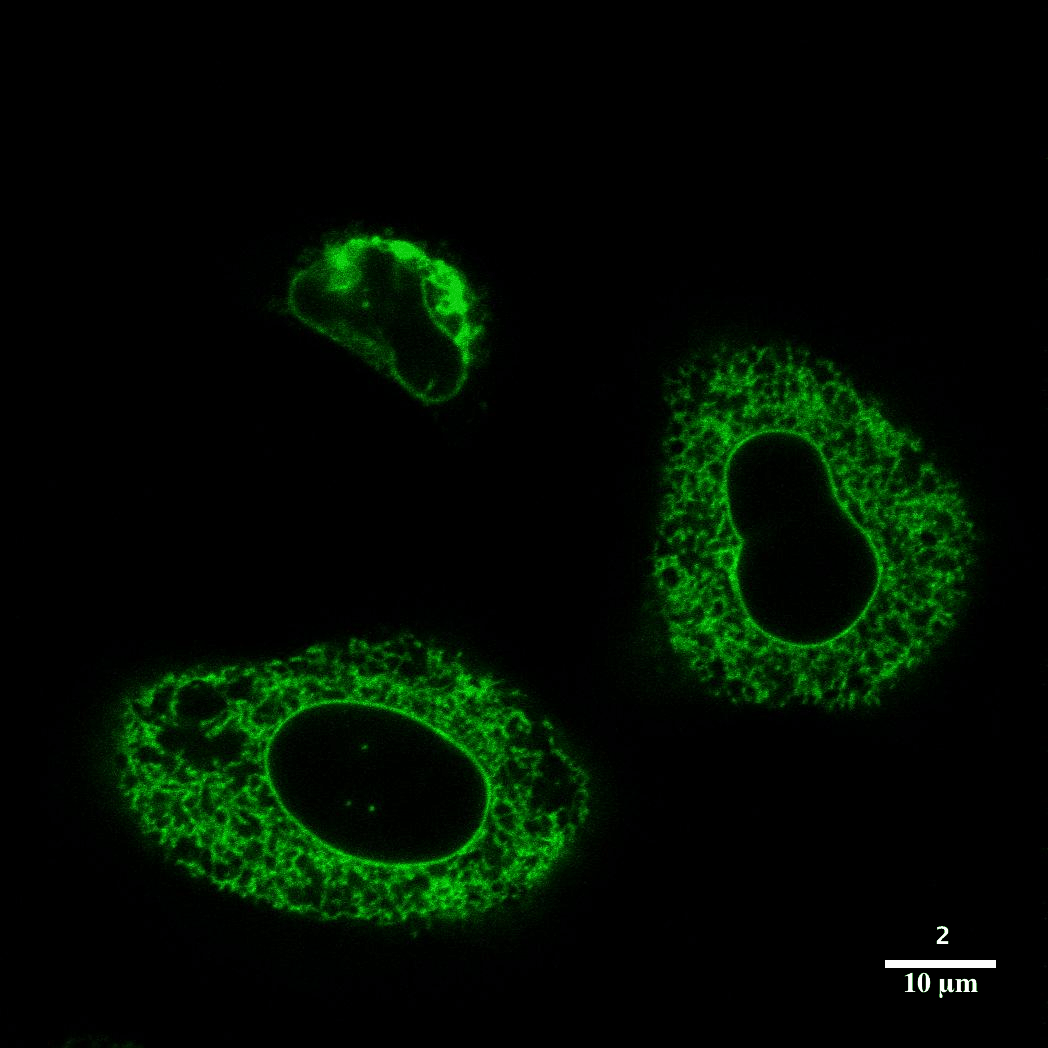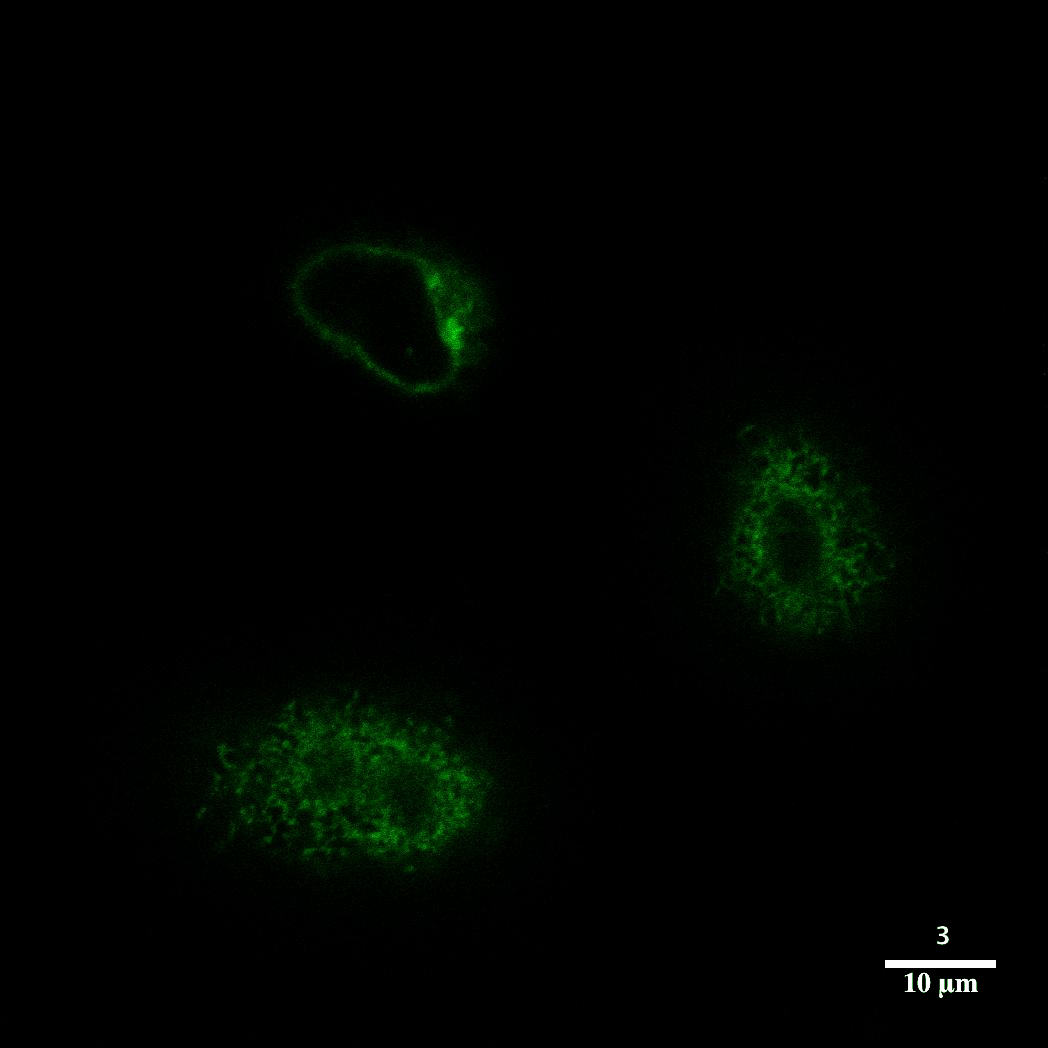 Optical SectioningConfocal microscopy is best utilized to provide optical sectioning of fluorescent samples. HeLa cells imaged here through Z were transfected with the construct sec61b-gfp. |
 Brainbow - Mouse - Amygdala |  Drosophila - X,Y, Z Confocal 1 of 2Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of three fluorescent channels separated by channel and combined as a three channel composite in the image on the pane to the far right The fly was fixed and labeled with neural markers and stained with DAPI to identify cell nuclei. |  Drosophila - X,Y, Z WidefieldThree dimensional imaging with a traditional fluorescent microscope yields poor results with very little optical sectioning. Confocal microscopy and structured illumination techniques enable optical sectioning for dramatically improved axial resolution. |
 Advanced Bacterial GenomicsExciting first glimpse of fresh data! Results are from forward genetic screening of bacteria labeled with GFP. The image in the center pane has some cells that show polar body localization. |  Mouse Developmental BiologyThis mouse embryo is roughly at developmental stage E8.5. The sample is immuno-labeled with various developmental markers to gain understanding of factors present during development. |  Basal DendritesMaximum projections of basal dendrites acquired in 3D with a 40x oil objective on a confocal microscope. |
 Clover division |  Plant Cell MitosisThis transgenic plant cell is labeled with yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) fused to tubulin. This image was acquired on a wide-field fluorescent microscope. Auto-fluorescence in plants can make fluorescence imaging tricky. Methods to overcome this hurdle include spectral imaging and/or digital "un-mixing" of spurious signals. |  Line-Scan Measuring Ca+ flux |
 Maggot FiletsThese are various maggot filet preps imaged with the contrast mechanism, Nomarski Differential-Interference Contrast (DIC). This contrasting technique uses polarized light in addition to prisms to give contrast to thin, clear samples. These filet preps are used to study nervous system development in fruit-flies. Morphological comparisons are made to identify developmental maladies. |  |  Cell Biology - fluorescent imagingHeLa cells transiently transfected with over-expression vectors for Sec61b-eGFP and aTubulin-mCherry. |
 Vesicular TransportThis is an extreme close up of a gfp-fusion construct that is involved in vesicular transport. |  Fly Muscles |
bottom of page